|
|
 |
Post-quake status of the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Station (Report #20)
-
Activities of JANTI’s SANE Committee (FY2009) - |
Jun 30, 2010
Rev.0
Japan Nuclear Technology Institute |
|
About three years have passed since Nigataken-chuetsuoki Earthquake occurred, and today, Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Units 6 and 7 are in commercial operations after the completion of integrity assessment.
Japan Nuclear Technology Institute (JANTI) has been conducted the activities of the “Structural Integrity Assessment Committee for Nuclear Power Components experienced Niigata Chuetsu-Oki Earthquake (SANE)” (chaired by Toshiharu Nomoto, Professor Emeritus of the University of Tokyo, September 2007 established) with the aim of examining the structural integrity of important equipment subjected to a seismic load that exceeds the design-basis level, developing and implement appropriate measures, and sharing the valuable lessons learned from disasters widely with the parties concerned. The Committee consists of academic experts specializing in structural strength, inspection, earthquake resistance, architecture, civil engineering and other areas, and members from electric utilities and manufacturers.
In this report, the achievements of in FY2009 will be reported, which were compiled in another interim report released in April this year. Please refer to the report posted on the JANTI homepage.
(http://www.gengikyo.jp/KikakuKijun/NomotoIinkai/index.html ;Japanese only)
|
| |
|
| 1. |
FY2009 Activity Status |
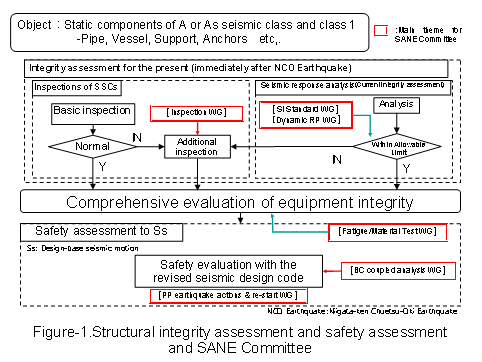
26 expert members from universities and academic societies and about 40 members from electric utilities and manufactures have participated in this Committee and continued to serve activities included a main framework for integrity assessment that combines inspection with analysis, data-based evaluation of fatigue breakdown modes, methods for measuring plastic strains, and fastener member inspection methods. As a result of these activities that were used indirectly in the integrity assessment report by TEPCO and various deliberation processes of the national government, the initial subjects of the Committee are being accomplished as a result of the activities.
The Committee held a total of three committee meetings by the end of FY2009. The six Working Groups (WGs) set up under the Committee convened meetings for a total of 15 sessions as appropriate to work on separate engineering issues. In this year, “Pre/post earthquake actions and re-start WG” was also set up and begun to study on the process of inspection/assessment based on the latest technology and lessons learned aimed at re-starting of Nuclear Power Plant (NPP) after earthquake. (See Table-1, Figure-1)
|
|
Table 1:
Scope and Activities of 6 WGs
| WG Name |
Main Subjects Examined by WG
|
| Structural integrity standard WG
|
Methods and standards for assessing structural integrity
|
| Inspection WG |
Methods for examining equipment’s plastic strains |
| Fatigue/Material test WG
|
Evaluation of fatigue strength of materials subjected to seismic load
|
| Building-Component Coupled analysis WG
|
Reasonable methods for evaluating reactor body foundations
|
| Pipe Vibration Evaluation WG
|
Evaluation of safety margins, e.g. piping damping coefficients, and reasonable piping design methods
|
| Pre/post earthquake actions and re-start WG |
Development of pre/post earthquake action guidelines |
|
|
 |
| |
|
| 2. |
Past Achievements |
In FY2009, the Committee was working on issues caused by design differences between ABWR and BWR-5 as the achievements for ABWR(Unit 6, 7) applied to BWR-5(Unit 1 to Unit 5), and start to organize guidelines by systematizing and generalizing separate engineering achievements for the convenience of the parties concerned. These engineering achievements are outlined below.
|
| |
|
| (1) |
Examination of Inspection Methods |
| |
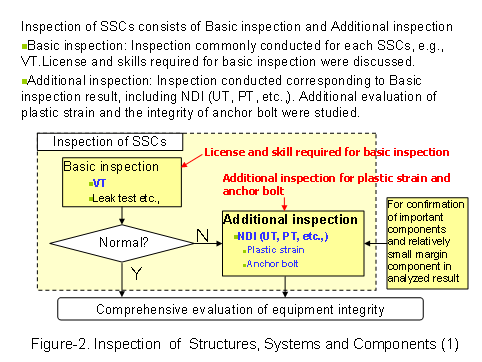
Inspection methods consists of Basic inspection (including visual checks, leak test, etc) and Additional inspection (including NDI, etc) examined for Unit 6 and Unit 7 were applied to the inspection on Unit 1 and Unit 5. As the result, there were no occurrences of plastic deformation at the inspection parts and the integrity of anchor bolts were confirmed. Moreover, the examination of inspection guideline was conducted, which was put together inspection methods and judging criteria against common Structure, Systems and Components (SSC’s), the view of license and skill required for Basic inspection. (See Figure-2, 3)
|
 |
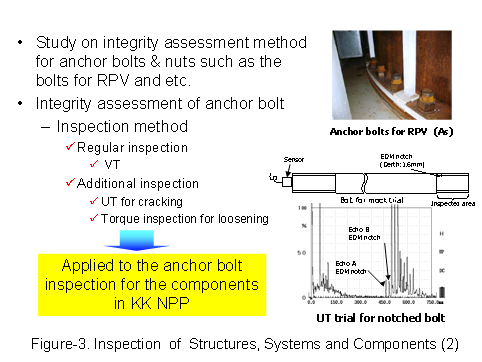 |
| |
|
| (2) |
Evaluating Seismic Resistance of Piping |
| |
In order to evaluate the integrity assessment and to judge continuous use of piping after earthquake, the examination of method for seismic assessment were carried out in ways to study on applicability of codes and standards that keeps reasonable safety margin and investigate on advanced elastic-plastic analysis for piping. (See Figure-4.)
|
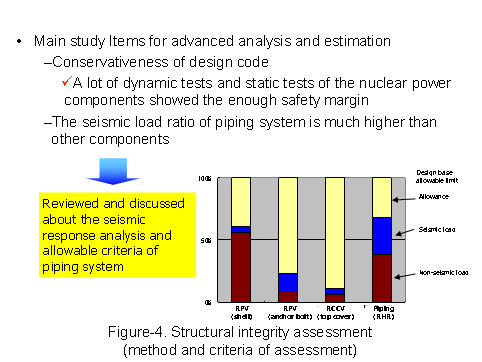
|
| |
Also in FY2009, to expand fatigue life data for a variety of materials and situations, the fatigue experimental data for three types of steels (SUS316NG, SFVQ1A, and STS410) were obtained and the assessment based on the accumulative fatigue coefficients in high temperature (300 Celsius degree) was secured to be acceptable. (See Figure-5, 6) |
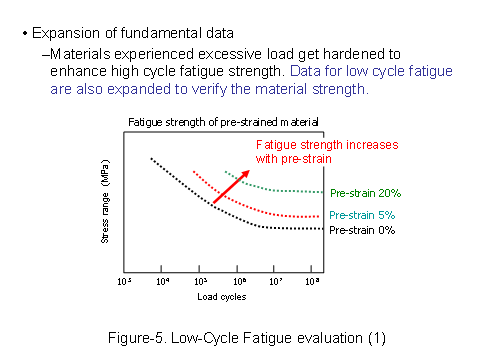 |
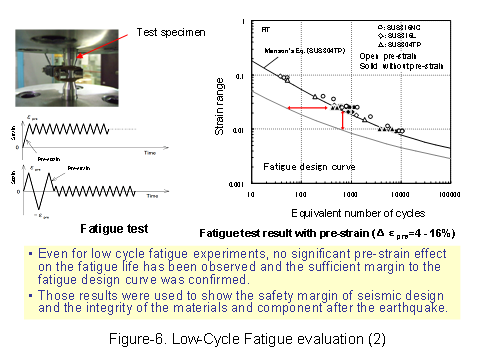 |
| |
Additionally, as a deformation case of outdoor piping with low seismic grade level, the integrity assessment of Mitered bends at the bottom of Circulation Water piping was conducted and evaluated to allow for its continuous use. (See Figure-7) |
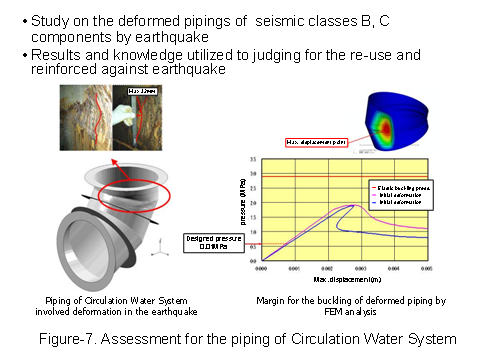 |
| |
|
| (3) |
Seismic Safety Assessment of RPV Pedestal by Elastic-Plastic Analysis for BWR-5 |
| |
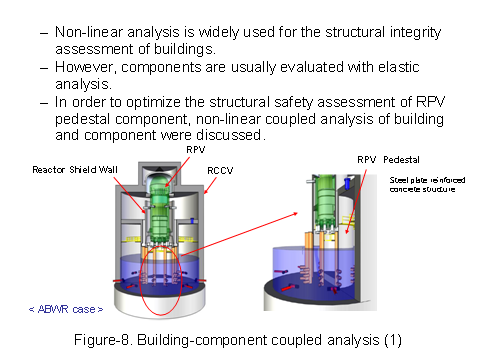
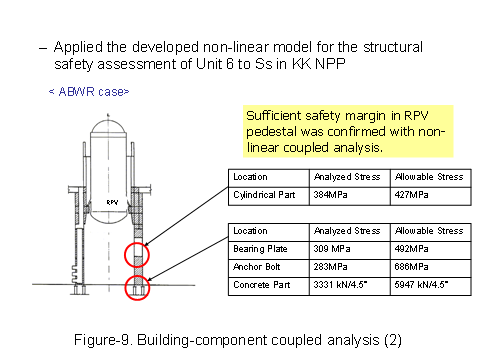
In a seismic response analysis coupling the reactor building, reactor containment vessel, RPV pedestal, and others, coupled seismic response analysis was conventionally performed using the elastic-plastic model for the reactor building and the elastic model for the RPV pedestal. On the BWR-5 analysis, an elastic-plastic analysis model was developed, taking into account the structural type of the RPV pedestal based on the result for ABWR (See Figure-8, 9).
This method was applied to the evaluation of the BWR-5 RPV pedestal against the design-basis seismic motion Ss. As a result, reasonable analysis results were obtained and seismic safety against the design-basis seismic motion Ss was confirmed.
|
|
 |
| |
|
| (4) |
Study for plant re-start up after earthquake |
| |
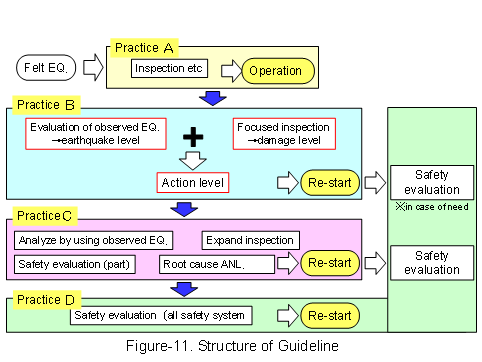
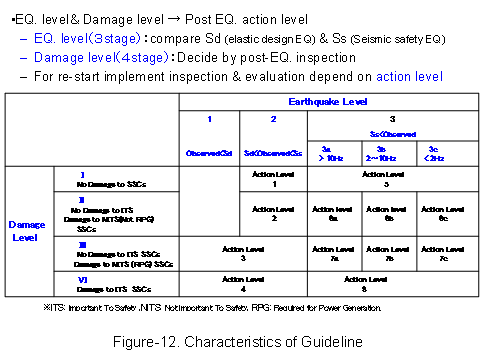
On the basis of domestic earthquake experiences and oversea trends of IAEA and EPRI, etc, the Committee has drafted action guidelines for re-starting of NPP after earthquake, on the view and procedure for inspection and evaluation in the period from earthquake occurred to re-starting, earthquake level and damage level of SSC’s were classified to each three and four stage, and then action levels for inspection and evaluation were made. (See Figure-10, 11, 12) |
|
|
 |
| |
| 3. |
Future Plan |
During a few Units in Kashiwazaki-Kariwa nuclear power station are resumption in operation, the initial subjects of the Committee are being accomplished. The Committee continues to serve the study for remaining issues and make efforts to enhance coordination with the societies concerned and information transmission.
In FY2010, as the grand sum of these activities, the Committee will be focused to schematize the obtained lessons learned and make the proposal guidelines to be consistent in the framework.
|
| |
|
| |
END |
|
|
|
|